CSS(Cascading Style Sheets):-
CSS Introduction:-
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen, paper, or in other media
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- External stylesheets are stored in CSS files
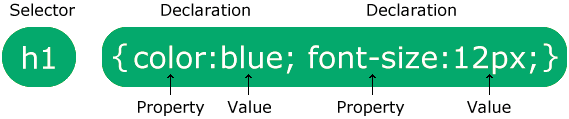
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
Example
In this example all <p> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}Try it Yourself »
In this example all <p> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}Try it Yourself »CSS Selectors:-
CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) the HTML elements you want to style.
We can divide CSS selectors into five categories:
- Simple selectors (select elements based on name, id, class)
- Combinator selectors (select elements based on a specific relationship between them)
- Pseudo-class selectors (select elements based on a certain state)
- Pseudo-elements selectors (select and style a part of an element)
- Attribute selectors (select elements based on an attribute or attribute value)
This page will explain the most basic CSS selectors.
The CSS element Selector
The element selector selects HTML elements based on the element name.
Example
Here, all <p> elements on the page will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
p {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »
Here, all <p> elements on the page will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
p {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »The CSS id Selector
The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
The id of an element is unique within a page, so the id selector is used to select one unique element!
To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
Example
The CSS rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1":
#para1 {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »Note: An id name cannot start with a number!
The CSS rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1":
#para1 {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »Note: An id name cannot start with a number!
The CSS class Selector
The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute.
To select elements with a specific class, write a period (.) character, followed by the class name.
Example
In this example all HTML elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
.center {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »
In this example all HTML elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
.center {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »You can also specify that only specific HTML elements should be affected by a class.
Example
In this example only <p> elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
p.center {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »
In this example only <p> elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
p.center {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »HTML elements can also refer to more than one class.
Example
In this example the <p> element will be styled according to class="center" and to class="large":
<p class="center large">This paragraph refers to two classes.</p>Try it Yourself »Note: A class name cannot start with a number!
In this example the <p> element will be styled according to class="center" and to class="large":
<p class="center large">This paragraph refers to two classes.</p>Try it Yourself »Note: A class name cannot start with a number!
The CSS Universal Selector
The universal selector (*) selects all HTML elements on the page.
Example
The CSS rule below will affect every HTML element on the page:
* {
text-align: center;
color: blue;
}Try it Yourself »
The CSS rule below will affect every HTML element on the page:
* {
text-align: center;
color: blue;
}Try it Yourself »The CSS Grouping Selector
The grouping selector selects all the HTML elements with the same style definitions.
Look at the following CSS code (the h1, h2, and p elements have the same style definitions):
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}
p {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}It will be better to group the selectors, to minimize the code.
To group selectors, separate each selector with a comma.
Example
In this example we have grouped the selectors from the code above:
h1, h2, p {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »
In this example we have grouped the selectors from the code above:
h1, h2, p {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »All CSS Simple Selectors
Selector Example Example description #id #firstname Selects the element with id="firstname" .class .intro Selects all elements with class="intro" element.class p.intro Selects only <p> elements with class="intro" * * Selects all elements element p Selects all <p> elements element,element,.. div, p Selects all <div> elements and all <p> elements
Three Ways to Insert CSS:-
| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| #id | #firstname | Selects the element with id="firstname" |
| .class | .intro | Selects all elements with class="intro" |
| element.class | p.intro | Selects only <p> elements with class="intro" |
| * | * | Selects all elements |
| element | p | Selects all <p> elements |
| element,element,.. | div, p | Selects all <div> elements and all <p> elements |
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
External CSS
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the <link> element, inside the head section.
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the <link> element, inside the head section.
Example
External styles are defined within the <link> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension.
The external .css file should not contain any HTML tags.
Here is how the "mystyle.css" file looks:
External styles are defined within the <link> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension.
The external .css file should not contain any HTML tags.
Here is how the "mystyle.css" file looks:
"mystyle.css"
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: navy;
margin-left: 20px;
}Note: Do not add a space between the property value and the unit (such as margin-left: 20 px;). The correct way is: margin-left: 20px;
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: navy;
margin-left: 20px;
}Note: Do not add a space between the property value and the unit (such as margin-left: 20 px;). The correct way is: margin-left: 20px;
Internal CSS
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the <style> element, inside the head section.
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the <style> element, inside the head section.
Example
Internal styles are defined within the <style> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: linen;
}
h1 {
color: maroon;
margin-left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »
Internal styles are defined within the <style> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: linen;
}
h1 {
color: maroon;
margin-left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »Inline CSS
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
Example
Inline styles are defined within the "style" attribute of the relevant element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is a heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »Tip: An inline style loses many of the advantages of a style sheet (by mixing content with presentation). Use this method sparingly.
Inline styles are defined within the "style" attribute of the relevant element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is a heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Try it Yourself »Tip: An inline style loses many of the advantages of a style sheet (by mixing content with presentation). Use this method sparingly.
Multiple Style Sheets
If some properties have been defined for the same selector (element) in different style sheets, the value from the last read style sheet will be used.
Assume that an external style sheet has the following style for the <h1> element:
h1 {
color: navy;
}Then, assume that an internal style sheet also has the following style for the <h1> element:
h1 {
color: orange;
}
If some properties have been defined for the same selector (element) in different style sheets, the value from the last read style sheet will be used.
Assume that an external style sheet has the following style for the <h1> element:
h1 {
color: navy;
}Then, assume that an internal style sheet also has the following style for the <h1> element:
h1 {
color: orange;
}Example
If the internal style is defined after the link to the external style sheet, the <h1> elements will be "orange":
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
<style>
h1 {
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>Try it Yourself »
If the internal style is defined after the link to the external style sheet, the <h1> elements will be "orange":
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
<style>
h1 {
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>Try it Yourself »Example
However, if the internal style is defined before the link to the external style sheet, the <h1> elements will be "navy":
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: orange;
}
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
</head>Try it Yourself »
However, if the internal style is defined before the link to the external style sheet, the <h1> elements will be "navy":
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: orange;
}
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
</head>Try it Yourself »HTML and CSS Comments
Comments are used to explain the code, and may help when you edit the source code at a later date.
Comments are ignored by browsers.
A CSS comment is placed inside the <style> element, and starts with /* and ends with */:
Example
/* This is a single-line comment */
p {
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »You can add comments wherever you want in the code:
Example
p {
color: red; /* Set text color to red */
}Try it Yourself »Comments can also span multiple lines:
Example
/* This is
a multi-line
comment */
p {
color: red;
}
Try it Yourself »CSS Comments:-
Comments are used to explain the code, and may help when you edit the source code at a later date.
Comments are ignored by browsers.
A CSS comment is placed inside the <style> element, and starts with /* and ends with */:
Example
/* This is a single-line comment */
p {
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »
/* This is a single-line comment */
p {
color: red;
}Try it Yourself »You can add comments wherever you want in the code:
Example
p {
color: red; /* Set text color to red */
}Try it Yourself »
p {
color: red; /* Set text color to red */
}Try it Yourself »Comments can also span multiple lines:
Example
/* This is
a multi-line
comment */
p {
color: red;
}
Try it Yourself »CSS Color Names:-
/* This is
a multi-line
comment */
p {
color: red;
}
Try it Yourself »In CSS, a color can be specified by using a predefined color name:
TomatoOrangeDodgerBlueMediumSeaGreenGraySlateBlueVioletLightGray
CSS Background Color
In CSS, a color can be specified by using a predefined color name:
CSS Background Color
You can set the background color for HTML elements:
Hello World
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat. Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
You can set the background color for HTML elements:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat. Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Example
<h1 style="background-color:DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="background-color:Tomato;">Lorem ipsum...</p>
Try it Yourself »CSS Text Color
<h1 style="background-color:DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="background-color:Tomato;">Lorem ipsum...</p>Try it Yourself »
You can set the color of text:
You can set the color of text:
Hello World
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat.
Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat.
Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Example
<h1 style="color:Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="color:DodgerBlue;">Lorem ipsum...</p>
<p style="color:MediumSeaGreen;">Ut wisi enim...</p>Try it Yourself »
<h1 style="color:Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="color:DodgerBlue;">Lorem ipsum...</p>
<p style="color:MediumSeaGreen;">Ut wisi enim...</p>Try it Yourself »CSS Border Color
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World
Example
<h1 style="border:2px solid Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid Violet;">Hello World</h1>Try it Yourself »
<h1 style="border:2px solid Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid Violet;">Hello World</h1>Try it Yourself »CSS Color Values
In CSS, colors can also be specified using RGB values, HEX values, HSL values, RGBA values, and HSLA values:
Same as color name "Tomato":
rgb(255, 99, 71)#ff6347hsl(9, 100%, 64%)Same as color name "Tomato", but 50% transparent:
rgba(255, 99, 71, 0.5)hsla(9, 100%, 64%, 0.5)
In CSS, colors can also be specified using RGB values, HEX values, HSL values, RGBA values, and HSLA values:
Same as color name "Tomato":
Same as color name "Tomato", but 50% transparent:
<h1 style="background-color:rgb(255, 99, 71);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:#ff6347;">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsl(9, 100%, 64%);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:rgba(255, 99, 71, 0.5);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsla(9, 100%, 64%, 0.5);">...</h1>Try it Yourself »
<h1 style="background-color:rgb(255, 99, 71);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:#ff6347;">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsl(9, 100%, 64%);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:rgba(255, 99, 71, 0.5);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsla(9, 100%, 64%, 0.5);">...</h1>Try it Yourself »Learn more about Color Values
Example
Example
RGBA Value
Example
HEX Value
Example
Example
3 Digit HEX Value
Example
Example
Saturation:-
Example
Lightness
Example
Shades of Gray
Example
HSLA Value
Example
CSS background:-
CSS background-color
Example
Other Elements
Example
Opacity / Transparency
Example
Transparency using RGBA
CSS background-image:-
Example
Example
Example
CSS background-repeat:-
Example
Example
CSS background-repeat: no-repeat
Example
CSS background-position
Example
CSS background-attachment:-
Example
Example
CSS Border Style
Example
CSS Border Width:-
Example
CSS Border Color:-
Example
Specific Side Colors
Example
HEX Values
Example
RGB Values
Example
HSL Values
Example
The CSS margin properties are used to create space around elements, outside of any defined borders.
Margin - Individual Sides
Example
Margin - Shorthand Property
Example
Example
Example
Example
The auto Value
Example
The inherit Value
Example
CSS Padding:-
Padding - Individual Sides
Example
CSS Setting height and width
CSS height and width Values
CSS height and width Examples
Example
In CSS, the term "box model" is used when talking about design and layout.
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content. The image below illustrates the box model:
Explanation of the different parts:
- Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border - A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent
The box model allows us to add a border around elements, and to define space between elements.
Example
Demonstration of the box model:
div {
width: 300px;
border: 15px solid green;
padding: 50px;
margin: 20px;
} Try it Yourself »













0 Comments